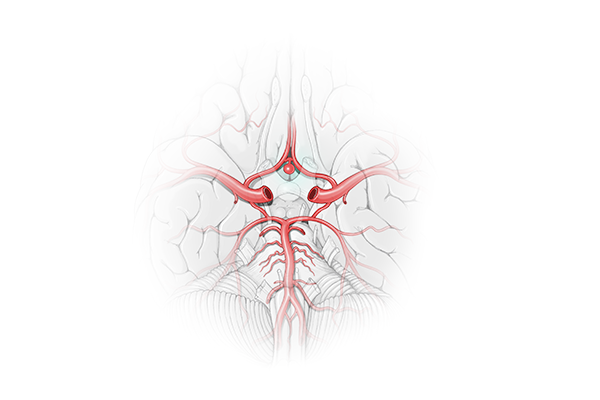
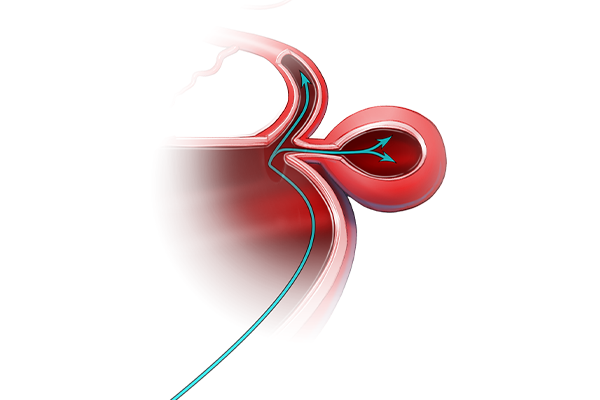
One in fifty people have an unruptured aneurysm.
What is a brain aneurysm?
A brain aneurysm is a bulge, or ballooning that develops in a weakened wall of a cerebral (brain) blood vessel, says Dr. Scott Rahimi, a Neurosurgery Specialist at Augusta University Health.
Causes of brain aneurysms
Brain aneurysms are not inherited, however, if more than one relative has an aneurysm, the risk of someone in the family having an aneurysm goes up.
A ruptured cerebral (brain) aneurysm causes a subarachnoid hemorrhage. This accounts for 3-5% of all new strokes. Around 10-30% of patients die before reaching the hospital.
People between the ages of 55-60 are most affected because of the pressure from blood flow causes the weakened area to bulge out and then rupture. Bleeding from a damaged blood vessel causes blood to accumulate at the surface of the brain in the subarachnoid space.
Warning signs
Some common warning signs that patients experience are:
- Sudden onset of a headache “the worst headache of my life” “thunderclap headache”
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
“One out of three people that have an aneurysm that ruptures die at home. Sometimes we incidentally find out about aneurysms through a CT scan or MRI brain.”
Prevention
Here are some ways to help prevent aneurysms:
- Blood pressure control
- Smoking cessation
- Decrease alcohol consumption
- Abstain from drug use
Treatment options
The good news is that there are treatment options available. Treatment options depend on various factors, such as size, type and location of the aneurysm. Treatment is the only way to prevent rebleeding. Treatment options include surgery and endovascular therapy.
- Surgery. Surgical clip is placed across the neck of the aneurysm. This prevents blood flow from entering the aneurysm.
- Endovascular therapy.
- Coil embolization – A catheter is threaded through the femoral artery, via a small skin incision near the groin. Coils are inserted into the aneurysm. This prevents blood flow from entering the aneurysm.
- Flow diverter stent – A flow diverter device is inserted into the parent artery, diverting the blood flow away from the aneurysm. This results in the aneurysm decreasing in size over time.
Augusta University Health treats 80-100 aneurysms per year. “Augusta University has had a lot of success treating aneurysms. The Augusta University Stroke center is an excellent resource for stroke care for our city.”
Augusta University Health treats 80-100 aneurysms per year. “Augusta University has had a lot of success treating aneurysms. The Augusta University Stroke Center is an excellent resource for stroke care for our city.”