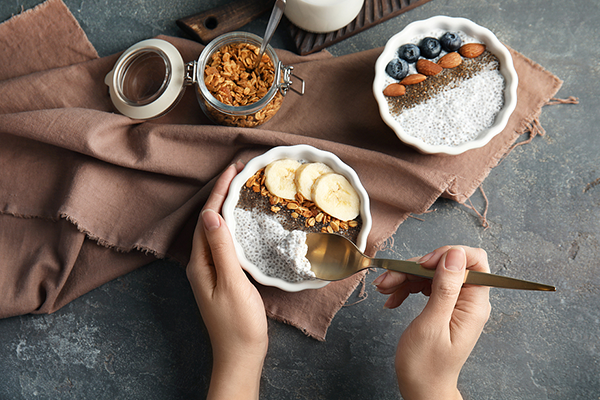
Fiber has always been said to be beneficial to our health, but how is this so?
To better explain the reasons why fiber is considered an essential nutrient for health maintenance, we must begin by explaining a little bit about what fiber actually is.
What exactly is fiber?
Fiber, or dietary fiber, can be defined as the non-digestible carbohydrate found in plant foods. Simply put, fiber encompasses all of the parts of a plant that cannot be broken down and absorbed by our bodies. There are 2 subcategories in which fiber can be divided into:
- Soluble fiber – This type of fiber attracts water and helps to slow down digestion. Soluble fiber can be found in oat bran, barley, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, peas, psyllium, and some fruits and vegetables.
- Insoluble fiber – This type of fiber repels water and passes through the gastrointestinal tract quickly. Insoluble fiber can be found in whole-wheat flour, wheat bran, nuts, beans, vegetables, and the skin of fruits.
Smart tip!
An easy way to remember the difference between soluble and insoluble fiber is to think of an apple. Apples contain both soluble and insoluble fiber.
- The skin of the apple provides insoluble fiber – This rough exterior does not dissolve in water.
- The flesh of the apple contains soluble fiber – This portion retains the most moisture.
What are the health benefits?
Now that we are more familiar with what fiber is, let’s dive into a few of the major health benefits that we can obtain from eating fiber every day:
- Fiber is essential for feeding the “good” bacteria found in our gut
The gastrointestinal tract is home to over 500 different species of bacteria that work to aid in the digestive process and help us utilize the nutrients we take in. By consuming fiber, we are feeding that good bacteria in order for them to continue their work towards keeping us healthy. Additionally, many of the bacteria that work in our bodies are vital in helping control our weight, blood sugar control, immune function and even brain function.
- Eating fiber helps to reduce constipation
Insoluble fiber helps to speed up the transit of food in the digestive tract and assists in preventing constipation. Additionally, soluble fiber found in oats, nuts, seeds, and other foods increase the water content of stool and can also provide a laxative effect. It is important to note however, that consuming fiber in excess and not drinking enough water can add to the dry mass of stool and may actually have a constipating effect.
- Fiber is associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer
It is known that colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. Research now demonstrates that eating foods containing fiber convincingly protect against this type of cancer. Whole, high-fiber foods contain various other healthy nutrients and antioxidants that may also impact cancer risk and help to keep the colon wall clean and healthy. Eating fiber also leaves byproducts produced by the “good” bacteria such as butyrate, which has demonstrated to be linked to reduced colorectal cancer risk.
How much fiber do you need?
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics recommends that women consume 21 to 25 grams of fiber a day, and men consume 30 to 38 grams a day. A food is considered high in fiber when it contains greater than 5 grams of fiber per serving.
A few high fiber foods include:
- 1/2 cup cooked kidney beans – 7 grams
- 1 cup of raspberries – 6.5 grams
- 1 cup of lentils – 13.1 grams
- 1 cup of raw oats – 16.5 grams
- 1 cup of popcorn – 14.4 grams
- 1 oz of chia seeds – 9.75 grams
So how do you add fiber into your diet? Here are some quick tips:
- Aim for 2+ servings of vegetables at lunch and dinner
- Swap in whole grain or whole-wheat foods into your diet – such as pasta, rice, and breads.
- Have a serving of fruit for dessert instead of a cookie or piece of cake
Gradual and small changes such as these can easily increase your fiber intake to your daily recommended amount. Just remember to increase your water intake as you do so. This will keep your gut happy and healthy!